
contentanalysis is a comprehensive R package designed
for in-depth analysis of scientific literature. It bridges the gap
between raw PDF documents and structured, analyzable data by combining
advanced text extraction, citation analysis, and bibliometric enrichment
from external databases.
AI-Enhanced PDF Import: The package supports AI-assisted PDF text extraction through Google’s Gemini API, enabling more accurate parsing of complex document layouts. To use this feature, you need to obtain an API key from Google AI Studio.
Integration with bibliometrix: This package
complements the science mapping analyses available in
bibliometrix and its Shiny interface
biblioshiny. If you want to perform content analysis within
a user-friendly Shiny application with all the advantages of an
interactive interface, simply install bibliometrix and
launch biblioshiny, where you’ll find a dedicated
Content Analysis menu that implements all the analyses
and outputs of this library.
The package goes beyond simple PDF parsing by creating a multi-layered analytical framework:
Intelligent PDF Processing: Extracts text from multi-column PDFs while preserving document structure (sections, paragraphs, references)
Citation Intelligence: Detects and extracts citations in multiple formats (numbered, author-year, narrative, parenthetical) and maps them to their precise locations in the document
Bibliometric Enrichment: Automatically retrieves and integrates metadata from external sources:
Citation-Reference Linking: Implements sophisticated matching algorithms to connect in-text citations with their corresponding references, handling various citation styles and ambiguous cases
Context-Aware Analysis: Extracts the textual context surrounding each citation, enabling semantic analysis of how references are used throughout the document
Network Visualization: Creates interactive networks showing citation co-occurrence patterns and conceptual relationships within the document
PDF Document → Text Extraction → Citation Detection → Reference Parsing
↓
CrossRef/OpenAlex APIs
↓
Citation-Reference Matching → Enriched Dataset
↓
Network Analysis + Text Analytics + Bibliometric IndicatorsThe result is a rich, structured dataset that transforms a static PDF into an analyzable knowledge object, ready for: - Content analysis: Understanding what concepts and methods are discussed - Citation analysis: Examining how knowledge is constructed and referenced - Temporal analysis: Tracking the evolution of ideas through citation patterns - Network analysis: Visualizing intellectual connections - Readability assessment: Evaluating text complexity and accessibility
[1],
[1-3], [1,5,7](Smith, 2020),
(Smith et al., 2020)Smith (2020) demonstrated...(see Smith, 2020; Jones et al., 2021)You can install the development version from GitHub:
# install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("massimoaria/contentanalysis")Complete workflow analyzing a real scientific paper:
library(contentanalysis)The paper is an open access article by Aria et al.:
Aria, M., Cuccurullo, C., & Gnasso, A. (2021). A comparison among interpretative proposals for Random Forests. Machine Learning with Applications, 6, 100094.
paper_url <- "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/massimoaria/contentanalysis/master/inst/examples/example_paper.pdf"
download.file(paper_url, destfile = "example_paper.pdf", mode = "wb")doc <- pdf2txt_auto("example_paper.pdf",
n_columns = 2,
citation_type = "author_year")
#> Using 17 sections from PDF table of contents
#> Found 16 sections: Preface, Introduction, Related work, Internal processing approaches, Random forest extra information, Visualization toolkits, Post-Hoc approaches, Size reduction, Rule extraction, Local explanation, Comparison study, Experimental design, Analysis, Conclusion, Acknowledgment, References
#> Normalized 77 references with consistent \n\n separators
# Check detected sections
names(doc)
#> [1] "Full_text" "Preface"
#> [3] "Introduction" "Related work"
#> [5] "Internal processing approaches" "Random forest extra information"
#> [7] "Visualization toolkits" "Post-Hoc approaches"
#> [9] "Size reduction" "Rule extraction"
#> [11] "Local explanation" "Comparison study"
#> [13] "Experimental design" "Analysis"
#> [15] "Conclusion" "Acknowledgment"
#> [17] "References"analysis <- analyze_scientific_content(
text = doc,
doi = "10.1016/j.mlwa.2021.100094",
mailto = "your@email.com",
citation_type = "author_year"
)
#> Extracting author-year citations only
#> Attempting to retrieve references from CrossRef...
#> Successfully retrieved 33 references from CrossRef
#> Fetching Open Access metadata for 14 DOIs from OpenAlex...
#> Successfully retrieved metadata for 12 references from OpenAlexThis single function call:
analysis$summary
#> $total_words_analyzed
#> [1] 3473
#>
#> $unique_words
#> [1] 1312
#>
#> $citations_extracted
#> [1] 50
#>
#> $narrative_citations
#> [1] 15
#>
#> $parenthetical_citations
#> [1] 35
#>
#> $complex_citations_parsed
#> [1] 12
#>
#> $lexical_diversity
#> [1] 0.3777714
#>
#> $average_citation_context_length
#> [1] 3186.16
#>
#> $citation_density_per_1000_words
#> [1] 6.57
#>
#> $references_parsed
#> [1] 33
#>
#> $citations_matched_to_refs
#> [1] 43
#>
#> $match_quality
#> # A tibble: 3 × 3
#> match_confidence n percentage
#> <chr> <int> <dbl>
#> 1 high 43 86
#> 2 no_match_author 6 12
#> 3 no_match_year 1 2
#>
#> $citation_type_used
#> [1] "author_year"readability <- calculate_readability_indices(doc$Full_text, detailed = TRUE)
readability
#> # A tibble: 1 × 12
#> flesch_kincaid_grade flesch_reading_ease automated_readability_index
#> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 12.4 33.9 11.8
#> # ℹ 9 more variables: gunning_fog_index <dbl>, n_sentences <int>,
#> # n_words <int>, n_syllables <dbl>, n_characters <int>,
#> # n_complex_words <int>, avg_sentence_length <dbl>,
#> # avg_syllables_per_word <dbl>, pct_complex_words <dbl>analysis$citation_metrics$type_distribution
#> # A tibble: 10 × 3
#> citation_type n percentage
#> <chr> <int> <dbl>
#> 1 parsed_from_multiple 12 24
#> 2 author_year_basic 9 18
#> 3 author_year_and 8 16
#> 4 narrative_etal 7 14
#> 5 author_year_etal 3 6
#> 6 narrative_three_authors_and 3 6
#> 7 narrative_two_authors_and 3 6
#> 8 narrative_four_authors_and 2 4
#> 9 see_citations 2 4
#> 10 doi_pattern 1 2head(analysis$citation_contexts[, c("citation_text_clean", "section", "full_context")])
#> # A tibble: 6 × 3
#> citation_text_clean section full_context
#> <chr> <chr> <chr>
#> 1 (Mitchell, 1997) Introduction on their own and make…
#> 2 (Breiman, Friedman, Olshen, & Stone, 1984) Introduction are supervised learni…
#> 3 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mlwa.2021.100094 Introduction author E mail address…
#> 4 (Breiman, 2001) Introduction node of a random subs…
#> 5 (see Breiman, 1996) Introduction single training set a…
#> 6 (Hastie, Tibshirani, & Friedman, 2009) Introduction by calculating predic…Create interactive network visualizations showing how citations co-occur within your document:
# Create citation network
network <- create_citation_network(
citation_analysis_results = analysis,
max_distance = 800, # Max distance between citations (characters)
min_connections = 2, # Minimum connections to include a node
show_labels = TRUE
)
# Display interactive network
network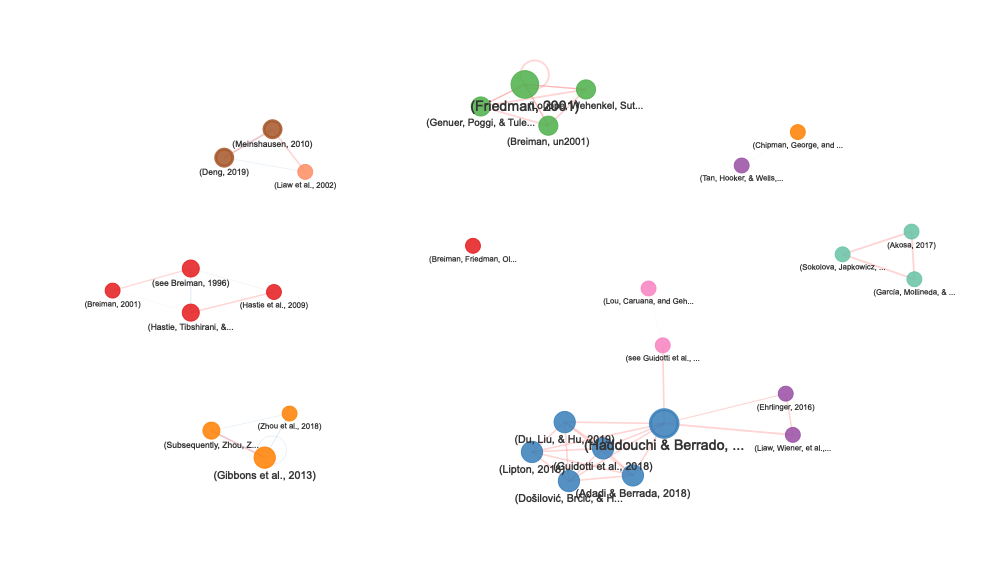
stats <- attr(network, "stats")
# Network size
cat("Nodes:", stats$n_nodes, "\n")
#> Nodes: 30
cat("Edges:", stats$n_edges, "\n")
#> Edges: 48
cat("Average distance:", stats$avg_distance, "characters\n")
#> Average distance: 227 characters
# Citations by section
print(stats$section_distribution)
#> primary_section n
#> 1 Related work 6
#> 2 Introduction 5
#> 3 Random forest extra information 4
#> 4 Size reduction 4
#> 5 Experimental design 3
#> 6 Visualization toolkits 3
#> 7 Local explanation 2
#> 8 Rule extraction 2
#> 9 Analysis 1
# Multi-section citations
if (nrow(stats$multi_section_citations) > 0) {
print(stats$multi_section_citations)
}
#> citation_text
#> 1 (Haddouchi & Berrado, 2019)
#> 2 (Meinshausen, 2010)
#> 3 (Deng, 2019)
#> sections n_sections
#> 1 Related work, Random forest extra information, Rule extraction 3
#> 2 Rule extraction, Comparison study, Analysis 3
#> 3 Rule extraction, Comparison study, Analysis 3The citation network visualization includes:
# Focus on very close citations only
network_close <- create_citation_network(
analysis,
max_distance = 300,
min_connections = 1
)
# Show only highly connected citations
network_hubs <- create_citation_network(
analysis,
max_distance = 1000,
min_connections = 5
)
# Hide labels for cleaner visualization
network_clean <- create_citation_network(
analysis,
show_labels = FALSE
)method_terms <- c("machine learning", "regression", "validation", "dataset")
word_dist <- calculate_word_distribution(doc, method_terms)# Create and save the plot
p <- plot_word_distribution(word_dist, plot_type = "line", smooth = TRUE, show_points = TRUE)
# Save as static image for GitHub
if (!dir.exists("man/figures")) dir.create("man/figures", recursive = TRUE)
htmlwidgets::saveWidget(p, "temp_plot.html", selfcontained = TRUE)
webshot::webshot("temp_plot.html", "man/figures/README-word-distribution.png",
vwidth = 1000, vheight = 600)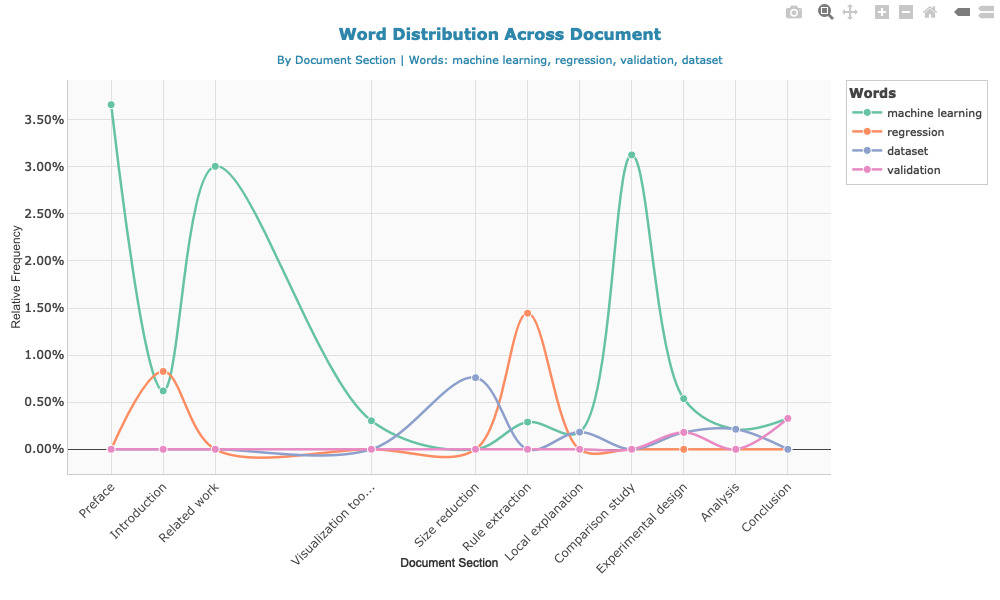
file.remove("temp_plot.html")
#> [1] TRUE
head(analysis$word_frequencies, 10)
#> # A tibble: 10 × 4
#> word n frequency rank
#> <chr> <int> <dbl> <int>
#> 1 model 45 0.0130 1
#> 2 forest 42 0.0121 2
#> 3 accuracy 40 0.0115 3
#> 4 trees 38 0.0109 4
#> 5 random 34 0.00979 5
#> 6 learning 27 0.00777 6
#> 7 set 27 0.00777 7
#> 8 variable 26 0.00749 8
#> 9 data 25 0.00720 9
#> 10 rule 25 0.00720 10head(analysis$network_data)
#> # A tibble: 6 × 5
#> citation1 citation2 distance type1 type2
#> <chr> <chr> <int> <chr> <chr>
#> 1 (Mitchell, 1997) (Breiman, Fri… 701 auth… auth…
#> 2 (Mitchell, 1997) https://doi.o… 992 auth… doi_…
#> 3 (Breiman, Friedman, Olshen, & Stone, 1984) https://doi.o… 250 auth… doi_…
#> 4 (Breiman, 2001) (see Breiman,… 257 auth… see_…
#> 5 (Breiman, 2001) (Hastie, Tibs… 617 auth… auth…
#> 6 (Breiman, 2001) (Hastie et al… 829 auth… auth…# View parsed references (enriched with CrossRef and OpenAlex)
head(analysis$parsed_references[, c("ref_first_author", "ref_year", "ref_journal", "ref_source")])
#> ref_first_author ref_year ref_journal ref_source
#> 1 Adadi 2018 IEEE Access crossref
#> 2 <NA> <NA> <NA> crossref
#> 3 Branco 2016 ACM Computing Surveys crossref
#> 4 Breiman 1996 Machine Learning crossref
#> 5 Breiman 2001 Machine Learning crossref
#> 6 Breiman 1984 International Group crossref
# Check data sources
table(analysis$parsed_references$ref_source)
#>
#> crossref
#> 33The ref_source column indicates where the data came
from:
"crossref": Retrieved from CrossRef API"parsed": Extracted from document’s reference
section# View citation-reference matches with confidence levels
library(dplyr)
#>
#> Attaching package: 'dplyr'
#> The following objects are masked from 'package:stats':
#>
#> filter, lag
#> The following objects are masked from 'package:base':
#>
#> intersect, setdiff, setequal, union
head(analysis$citation_references_mapping[, c("citation_text_clean", "ref_authors",
"ref_year", "match_confidence")])
#> # A tibble: 6 × 4
#> citation_text_clean ref_authors ref_year match_confidence
#> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr>
#> 1 (Mitchell, 1997) Mitchell 1997 high
#> 2 (Breiman, Friedman, Olshen, & Stone, 19… Breiman 1984 high
#> 3 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mlwa.2021.100… <NA> <NA> no_match_year
#> 4 (Breiman, 2001) Breiman, L. 2001 high
#> 5 (see Breiman, 1996) Breiman, L. 1996 high
#> 6 (Hastie, Tibshirani, & Friedman, 2009) Hastie 2009 high
# Match quality distribution
table(analysis$citation_references_mapping$match_confidence)
#>
#> high no_match_author no_match_year
#> 43 6 1# Find all citations to works by Smith
analysis$citation_references_mapping %>%
filter(grepl("Smith", ref_authors, ignore.case = TRUE)) %>%
select(citation_text_clean, ref_full_text, match_confidence)
#> # A tibble: 0 × 3
#> # ℹ 3 variables: citation_text_clean <chr>, ref_full_text <chr>,
#> # match_confidence <chr># If OpenAlex data was retrieved
if (!is.null(analysis$references_oa)) {
# View enriched metadata
head(analysis$references_oa[, c("title", "publication_year", "cited_by_count",
"type", "oa_status")])
# Analyze citation impact
summary(analysis$references_oa$cited_by_count)
}
#> Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
#> 94.0 205.5 1089.0 12844.9 7064.2 114163.0analysis$citation_metrics$section_distribution
#> # A tibble: 15 × 3
#> section n percentage
#> <fct> <int> <dbl>
#> 1 Preface 0 0
#> 2 Introduction 7 14
#> 3 Related work 9 18
#> 4 Internal processing approaches 0 0
#> 5 Random forest extra information 6 12
#> 6 Visualization toolkits 4 8
#> 7 Post-Hoc approaches 0 0
#> 8 Size reduction 6 12
#> 9 Rule extraction 3 6
#> 10 Local explanation 5 10
#> 11 Comparison study 2 4
#> 12 Experimental design 4 8
#> 13 Analysis 4 8
#> 14 Conclusion 0 0
#> 15 Acknowledgment 0 0# Track disease-related terms
disease_terms <- c("covid", "pandemic", "health", "policy", "vaccination")
dist <- calculate_word_distribution(doc, disease_terms, use_sections = TRUE)
# View frequencies by section
dist %>%
select(segment_name, word, count, percentage) %>%
arrange(segment_name, desc(percentage))
#> # A tibble: 1 × 4
#> segment_name word count percentage
#> <chr> <chr> <int> <dbl>
#> 1 Conclusion health 1 0.328
# Visualize trends
#plot_word_distribution(dist, plot_type = "area", smooth = FALSE)pdf2txt_auto(): Import PDF with automatic section
detectionreconstruct_text_structured(): Advanced text
reconstructionextract_doi_from_pdf(): Extract DOI from PDF
metadataanalyze_scientific_content(): Comprehensive content and
citation analysis with API enrichmentparse_references_section(): Parse reference list from
textmatch_citations_to_references(): Match citations to
references with confidence scoringget_crossref_references(): Retrieve references from
CrossRef APIcreate_citation_network(): Create interactive citation
co-occurrence networkcalculate_readability_indices(): Compute readability
scores (Flesch, Gunning Fog, SMOG, Coleman-Liau)calculate_word_distribution(): Track word frequencies
across document sectionsreadability_multiple(): Batch readability analysis for
multiple documentsplot_word_distribution(): Interactive visualization of
word distribution across sectionsget_example_paper(): Download example paper for
testingmap_citations_to_segments(): Map citations to document
sections/segmentsThe package integrates with CrossRef’s REST API to retrieve structured bibliographic data:
https://api.crossref.org/works/{doi}/referencesmailto parameter)OpenAlex provides comprehensive scholarly metadata:
openalexR packageopenalexR::oa_apikey()# For CrossRef (recommended to avoid rate limits)
analysis <- analyze_scientific_content(
text = doc,
doi = "10.xxxx/xxxxx",
mailto = "your@email.com" # Your email for CrossRef polite pool
)
# For OpenAlex (optional, increases rate limits)
# Get free API key at: https://openalex.org/
openalexR::oa_apikey("your-api-key-here")Core: pdftools, dplyr, tidyr, stringr, tidytext, tibble, httr2, visNetwork, openalexR
Suggested: plotly, RColorBrewer, scales (for visualization)
If you use this package in your research, please cite:
Massimo Aria & Corrado Cuccurullo (2025). contentanalysis: Scientific Content and Citation Analysis from PDF Documents.
R package version 0.2.0.
https://doi.org/10.32614/CRAN.package.contentanalysisGPL (>= 3)
Please report issues at: https://github.com/massimoaria/contentanalysis/issues
Contributions are welcome! Please feel free to submit a Pull Request.